Stem cell therapy has emerged as one of the most promising advancements in regenerative medicine, particularly in the field of wound healing. Chronic wounds, especially diabetic foot ulcers, are a growing global concern due to their impact on patient mobility and quality of life. Traditional treatments have often been insufficient, making stem cell-based therapies a revolutionary alternative. This article explores the potential of stem cell therapy in promoting tissue regeneration and healing of chronic wounds.
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various types of specialized cells. These cells are essential in tissue repair and regeneration because they can differentiate into the specific types of cells needed to repair damaged tissues. There are several types of stem cells, including adult stem cells, embryonic stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), each with unique regenerative properties.
How Stem Cells Are Used in Tissue Bioengineering for Wound Healing:
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various types of specialized cells. These cells are essential in tissue repair and regeneration because they can differentiate into the specific types of cells needed to repair damaged tissues. There are several types of stem cells, including adult stem cells, embryonic stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), each with unique regenerative properties.
- Wound Healing Process
Chronic wounds often suffer from prolonged inflammation, insufficient tissue repair, and a lack of new blood vessel formation (vascularization). Stem cell therapy addresses these issues by promoting cell regeneration, collagen production, and angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels). - Types of Stem Cells in Use:
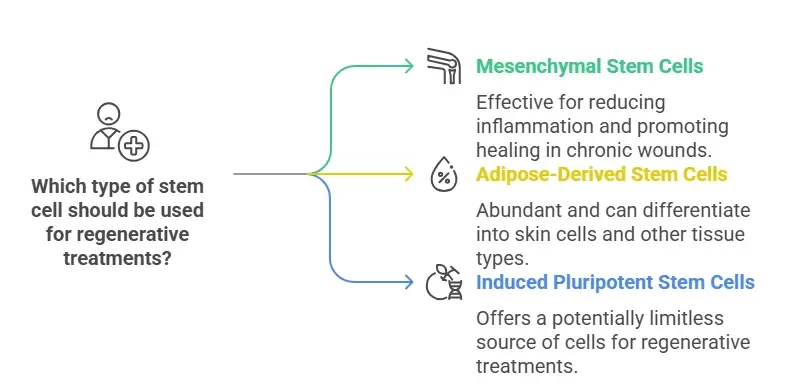
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): These stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including those needed for skin and tissue regeneration. MSCs play a key role in reducing inflammation and promoting healing in chronic wounds.
- Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs): These stem cells, sourced from fat tissue, are increasingly used in wound healing due to their abundance and ability to differentiate into skin cells and other tissue types.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): iPSCs can be reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells, offering a potentially limitless source of cells for regenerative treatments.
- Mechanisms of Action:
- Tissue Regeneration: Stem cells stimulate the formation of new tissues by promoting the proliferation of local cells.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Stem cells can reduce inflammation at the wound site, a critical factor in the healing of chronic wounds.
- Angiogenesis: Stem cells promote the formation of new blood vessels, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the healing tissue.

Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy in Wound Healing:

- Accelerated Healing: Stem cell therapy can significantly speed up the healing process, reducing the time needed for chronic wounds to close.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: By promoting faster regeneration of healthy tissue, stem cells help to close the wound faster, lowering the risk of infection.
- Minimized Scarring: Stem cell therapy can also minimize the formation of scars, improving both the aesthetic and functional outcomes of wound healing.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Regulatory Hurdles: While stem cell therapies have shown promise, they face significant regulatory hurdles before they can be widely adopted in clinical practice.
- Cost: Stem cell therapies can be expensive, and access to such treatments may be limited for some patients.
- Long-Term Efficacy: Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell treatments in wound healing.
Conclusion:
Stem cell therapy is paving the way for innovative approaches to wound healing and tissue regeneration, especially in the treatment of chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers. As research advances and regulatory barriers are overcome, stem cell-based therapies may become a cornerstone of regenerative medicine, offering patients faster and more effective healing options. At Everlast, we are at the forefront of incorporating cutting-edge tissue bioengineering solutions to revolutionize wound care and improve patient outcomes.

